The pulp and paper industry in India plays a vital role in the economy, producing a range of paper products for sectors like education, media, and packaging.
Pulp and Paper Industry
Introduction to the Pulp and Paper Industry in India
The pulp and paper industry in India plays an essential role in the economy, producing various products used for education, communication, packaging, and more. India is one of the top paper producers in the world, with a significant portion of the market catered to by both large and small manufacturers. The Indian paper industry has come a long way thanks to advancements in technology, raw material sourcing and production methods. Though it remains highly labor intensive, it is moving towards automation and sustainable practices. Pulp and Paper Industry . The growth of the sector coincides with the increase in literacy rate, urbanization and increasing demand for packaging materials.
The Indian paper industry includes many types of paper such as printing and writing paper, newsprint, tissue paper and paperboard used in packaging. Pulp and Paper Industry . The sector is also characterized by the use of a variety of raw materials such as wood, bamboo, agricultural waste such as bagasse and recycled paper.
Historical Development of the Pulp and Paper Industry in India
Indian cellulose and paper industry dates back to the beginning of the 19th century. The first paper factory in India was founded in 1812 in the scrimper, in Western Bengal. However, it was only after India gained independence in 1947 that the sector saw significant growth. In the 1950s and 1960s, paper mills were set up with the help of foreign investment and technology. Pulp and Paper Industry . The industry witnessed rapid growth from the 1970s, especially in the 1980s and 1990s, with the entry of major players such as Ballarpur Industries Limited (BILT) and ITC Limited. In the 21st century, the industry has undergone a transformation with the introduction of environment-friendly practices and modern technologies.

Types of Paper Products Produced in India
The Indian pulp and paper industry produces various types of paper products, each serving different purposes in the economy.
Printing and writing paper: This includes office paper, book paper, and other types used for publishing and printing. It constitutes the largest segment of the Indian paper industry.
Newsprint: Used primarily for newspapers, India imports a significant portion of its newsprint but also has a substantial domestic production.
Packaging Paper and Boards: India’s growing retail sector has led to a rise in the demand for packaging materials such as corrugated boxes and cartons.
Tissue Paper: With growing hygiene awareness, tissue paper consumption is increasing in India, especially in urban areas.
Specialty Papers: These include papers used for specific purposes like thermal papers, coated papers, and papers used for security features.
Raw Materials and Manufacturing Processes
The raw materials used in the Indian paper manufacturing industry vary depending on the type of paper produced. Traditionally, wooden pulp was the main raw material. However, due to deforestation issues and the high cost of wood, there has been a trend towards using agricultural waste such as bagasse, wheat straw and recycled paper. Pulp and Paper Industry .
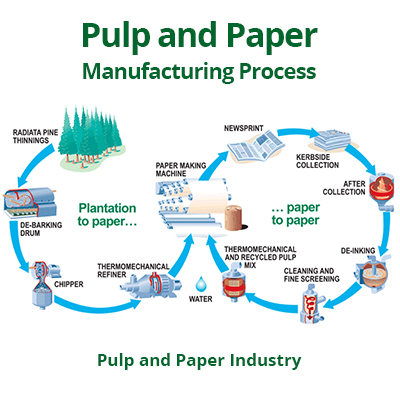
The paper production process involves several steps:
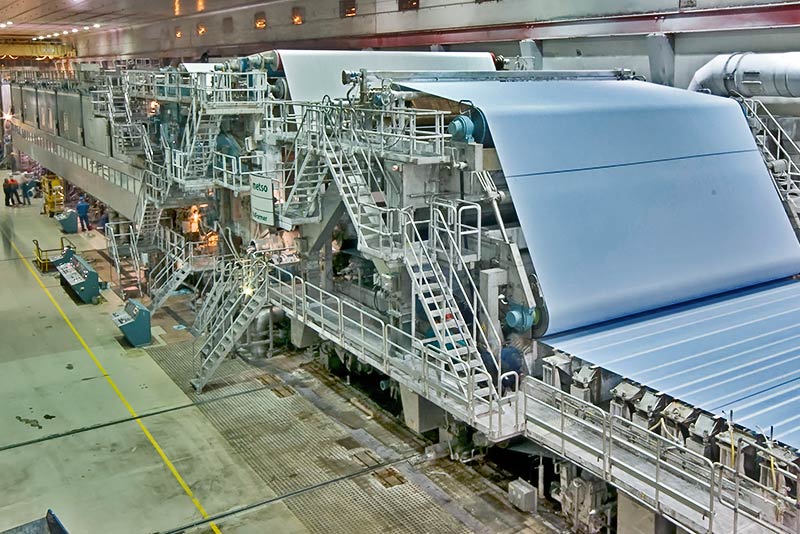
Pulp production: Raw materials are converted into cellulose, which is a suspension of fibers in water. Papermaking: The pulp is rolled out into thin sheets, which are then pressed, dried and rolled to form paper.
Finishing: The paper is cut to size and packaged for distribution.
Current Status of the Indian Pulp and Paper Industry
India is the 15th largest paper producer in the world with an annual production of over 15 million tonnes. The market is highly fragmented with around 700 mills, ranging from large integrated mills to smaller paper companies.
Challenges Facing the Indian Pulp and Paper Industry
Despite its growth, India’s paper and pulp industry faces several challenges.
Availability of raw materials: Dependence on imported wood and the cost of raw materials like bamboo and recycled paper pose challenges for manufacturers.
Environmental issues: Paper production is resource intensive requiring large amounts of water and energy. Additionally, the industry faces increasing pressure to adopt sustainable practices.
Regulatory issues: The Indian paper industry has to comply with strict environmental regulations, including waste management and air quality.
Government Policies and Regulations
The Indian government has implemented various policies to promote the growth of the pulp and paper industry, including providing tax incentives, research and development subsidies, and encouraging the use of renewable resources. Environmental rules such as the environment for monitoring pollution and water use also affect the sector. Pulp and Paper Industry .
Technological Innovations and Trends
The paper industry is implementing modern technologies such as automation, process optimization and recycling to improve efficiency. New trends such as the use of alternative raw materials such as agricultural waste, advances in water purification and energy consumption are contributing to making the industry more sustainable. Pulp and Paper Industry .
Environmental and Sustainability Concerns
Pulp and paper industry is known for its environmental award, including deworming, water consumption and waste production. To solve these problems, many companies have accepted a stable practice, such as the use of processed paper, a decrease in energy consumption and the use of cleaner technologies.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
The future of the Indian paper industry looks promising. With a growing domestic market, increasing export potential, and rising demand for sustainable products, the industry is poised for steady growth. The government’s focus on promoting environmentally friendly alternatives and sustainable practices will boost growth.
The Indian pulp and paper industry has grown significantly over the past few decades owing to the country’s growing population, rising literacy rate and increasing demand for paper products in various sectors like education, packaging, media etc. India is currently one of the largest paper producers in the world and contributes significantly to the country’s economy. As of 2023, India stands as the 15th largest producer of paper, with production levels exceeding 15 million tons annually.
The industry has evolved significantly over the past few decades, driven by advancements in technology, sustainability efforts, and growing demand in both domestic and international markets. India’s vast and diverse raw material base, including wood, bamboo, bagasse, and recycled paper, provides a competitive advantage, while also posing challenges related to resource management and environmental concerns. As the country’s literacy rate increases, the demand for paper products continues to grow, fueled by sectors such as e-commerce and packaging.
The industry in India is highly fragmented, with over 700 mills, ranging from large-scale integrated mills to smaller, regional mills. These mills produce various types of paper such as printing and writing paper, newsprint, tissue paper, packaging board and specialty paper. Pulp and Paper Industry .
The country’s huge demand for paper and board, driven by its thriving sectors such as education, retail, media and e-commerce, has made India a significant player in the global paper market. The growth of the pulp and paper industry in India dates back to the early 19th century, with the first paper mill being established in Seram pore, West Bengal, in 1812. However, it was with India’s independence in 1947, and especially since the 1970s, that the paper industry began to develop rapidly.
The establishment of large-scale mills with foreign investments and technology transferred from countries like Japan and Germany significantly boosted domestic production. The 1980s and 1990s saw the rise of major corporate players like Ballarpur Industries Limited (BILT) and ITC Limited, which further accelerated the industry’s development.
As time goes on, the market is more competitive, and domestic and international companies are gaining market share. India has continued to be urbanized, but the demand for paper has increased, especially in the retail packaging department promoted by high -activity electronic commercial industries.
The Indian pulp and paper industry uses a variety of raw materials including wood, bamboo, agricultural waste materials such as bagasse and wheat straw, and recycled paper. Traditionally, wood pulp was the primary raw material for paper production, but concerns over deforestation and rising timber prices have led to alternative sources becoming more popular in recent years. Bagos, a by -product of sugarcane treatment, is an important raw material for Indian paper factories for its abundance and profitability. Agricultural residues such as wheat straws and rice pods are also increasingly used as alternative fibers for paper production, reducing the dependence on the wood and dealing with sustainability issues.
The paper production process involves several key steps. First, the raw material is transformed into pulp, which is a suspension of fibers suspended in water. Next, this pulp is subject to a series of mechanical and chemical treatments to destroy fibers and eliminate impurities. Next, the pulp extends to a large flat screen, forms thin leaves, removes excess water, and dries with paper formation. In the final stages of production, the paper is cut into rolls or sheets, depending on the required product specifications. The paper is then packed and ready for distribution.
In recent years, there has been a major change in the technical achievements in the India’s pulp industry and the paper industry. The use of advanced mechanisms for paper factories and the processing of pulp processing and the adoption of effective energy technologies have played a role in improving productivity and reducing operational costs. In addition, many factories include stable practices, such as water treatment, energy recurrence, and discharge from production processes.
The use of enzymes for the development of new methods such as alkali reactors and the treatment of fiber has also contributed to the decrease in industrial impact on the environment while improving the final quality of the product. The implementation of Industry 4.0 practices, which involves the use of smart sensors, automation, and real-time monitoring, has allowed paper manufacturers to improve the quality of their products and enhance operational efficiency.
The cellulose and paper industry in India, like its global colleagues, is faced with a number of environmental problems. Paper production is by nature resource -intensive, requiring a large amount of water, energy and raw materials. In addition, it generates large amounts of waste, including chemical by-products, sludge and air pollutants. Pulp and Paper Industry .
The industry’s impacts on forests, water resources and air quality are of major concern to environmental activists and regulators. Deforestation due to the demand for wood pulp has long been a significant issue, particularly in India where forest area is declining rapidly. In response to these concerns, the industry has taken many steps to introduce more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices.
One of the biggest trends in the Indian paper industry is the increasing focus on using alternative, renewable raw materials. Using bamboo, bagasse and agricultural waste to produce paper has reduced pressure on forests and made the industry more environmentally friendly. In addition to raw materials, paper mills in India are also adopting energy-efficient practices to minimize their environmental impact. Many mills are investing in renewable energy sources such as biomass, solar, and wind power to power their operations.
Recycling of waste paper is also an important strategy that has gained momentum in recent years. The increased availability of recycled paper has reduced the need for virgin pulp, further reducing the industry’s environmental impact. Pulp and Paper Industry .
Water usage remains one of the biggest challenges for the Indian pulp and paper industry. Paper mills consume large quantities of water during the production process, especially during the pulping and paper forming stages. However, many companies are currently introducing water elimination systems to minimize their dependence on freshwater sources.
Water supply systems with a closed circuit, where water is treated and noted several times in the mill, becomes more and more frequent in the industry. In addition, treating wastewater before it is released into the environment has become a mandatory requirement for many factories. Efforts to reduce emissions, such as implementing air pollution controls and adopting cleaner technologies, are also contributing to improving environmental performance across the industry.
The Indian paper market has been growing steadily and demand is expected to continue to expand due to factors such as urbanization, rising literacy rates and rising demand for packaging materials from the paper retail industry and e-commerce. As disposable income increases and more people move into the middle class, consumption of paper products such as office supplies, books, newspapers and toilet paper is expected to grow significantly over the next few years. Growing electronic commercial sector contributes to the growing demand for packaging materials such as waveform boxes, boxes, and other wrapping products.
As per industry forecasts, the Indian paper and pulp industry is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 6-7% over the next decade, primarily due to the increasing demand for paper products in the domestic market and expanding export opportunities. Indian document factories are also increasingly providing exports not only in the internal market, but also to countries in countries in the Middle East, Africa, Southeast Asia, and countries in states and Europe.
Global demand for sectors such as paper tables and packaging materials, especially foods, drinks, pharmaceuticals, and electronic devices has created important opportunities for Indian paper manufacturers to expand their wallet exports. Pulp and Paper Industry .
Although domestic demand is expected to increase, issues such as imported paper products, especially competition from countries such as China and Indonesia, may be pressure on Indian manufacturers. Nevertheless, India’s cost -effective work, the possibility of acquiring alternative ingredients, and sustainable practice gives a competitive advantage in the industry.
Additionally, India’s government policies, including incentives for manufacturing and exporting eco-friendly products, are expected to support the industry\’s growth. The increasing focus on sustainable packaging materials and eco-friendly paper products offers new avenues for growth, particularly in the global market, where consumers and businesses are becoming more environmentally conscious.
Recognizing the economic importance of the pulp and paper industry, the Government of India has taken several steps to support the industry. Pulp and Paper Industry . Policies such as the National Policy on Paper and Board, which aims to promote the growth of the industry through measures such as technology investment, modernization and export promotion, have played a key role in shaping the development of the industry.
The government also offers various incentives, such as subsidies for research and development in papermaking technology and tax breaks for factories that adopt energy-efficient methods. In addition, policies aimed at promoting sustainability, such as the promotion of alternative raw materials and recycled paper, have encouraged the industry to adopt more environmentally friendly practices.
In terms of regulations, the paper industry in India is subject to stringent environmental standards aimed at reducing pollution and ensuring sustainable use of resources. The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and state pollution control boards regulate the discharge and emission of effluent from paper mills. Pulp and Paper Industry .
Compliance with environmental standards is crucial for the further operation of paper factories, and many companies invest in advanced technologies for controlling pollution to comply with these standards. The adoption of the expanded liability of manufacturers (EPR), which obliges manufacturers to take responsibility for the disposal and disposal of their products, is another significant regulation that forms the future of the industry.
The future of the Indian pulp and paper industry looks bright owing to strong growth in demand, opportunities for technological advancements and focus on sustainable development. The industry is poised for growth, especially in the packaging segment, driven by the rise of e-commerce and consumer demand for sustainable products. However, the sector must continue to address challenges such as raw material scarcity, water usage, and environmental concerns. If the industry continues to focus on innovation, sustainability, and expanding its export market, it will be well-positioned for continued success in the coming years.



